Ad Code
Translate
Five Do’s For a Healthy Turnover That Bolsters Talent-Retention
October 20, 2025
Smart strategies for trading on crypto exchanges
October 20, 2025
What is Ozempic (semaglutide)? (Updated in 2025)
January 30, 2025
Discover Honeybee Pharmacy (2025 Guide Important Consumer Tips)
October 14, 2025
Posture Bra: Improving Back Support and Comfort
October 20, 2025
How To Find Suitable Properties In Cyprus?
October 20, 2025
10 Effective Strategies to Improve Domain Authority of Your Website
October 20, 2025
The Role of Prototype Manufacturers in Advancing Sustainable Product Design
Khabza Mkhize
July 26, 2025
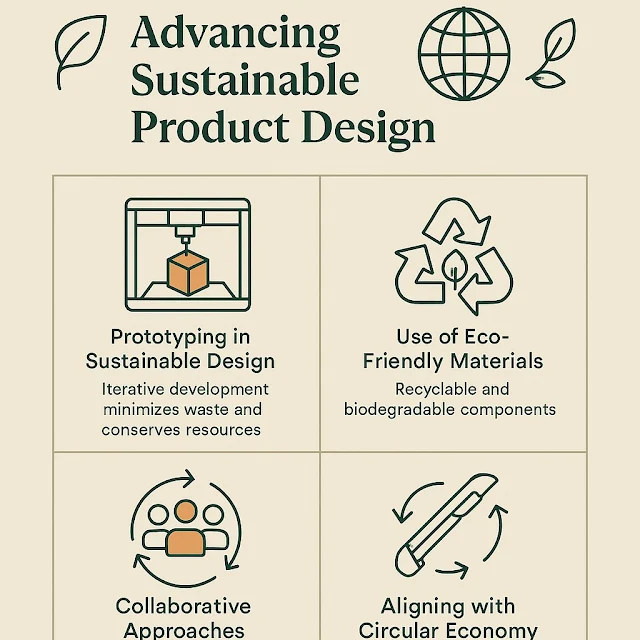
Introduction
In today’s global economy, sustainability is not just a trend—it’s a necessity. With increasing regulatory pressure, consumer awareness, and environmental urgency, industries are accelerating efforts to reduce their ecological footprint. At the core of this transformation is the prototype manufacturer, which is becoming instrumental in enabling sustainable innovation across sectors. Among them, Pepin Manufacturing has emerged as a leader, driving sustainable product development from ideation to production through advanced prototyping, eco-conscious materials, and collaborative innovation.
The Strategic Value of Prototyping in Sustainable Product Design
Prototyping represents a transformative and essential phase within the product development lifecycle, acting as a crucial bridge between initial concepts and mass production. This iterative process enables designers and engineers to visualise, test, and refine their ideas in tangible formats before finalisation. Through comprehensive prototyping, teams can thoroughly evaluate a product’s functionality, usability, and aesthetic appeal, ultimately enhancing both performance and user satisfaction.Moreover, this prototyping approach inherently fosters sustainability throughout the development lifecycle. The early identification of potential issues and the exploration of optimisation possibilities empower prototype manufacturers to significantly minimise waste and conserve essential resources. This proactive strategy not only streamlines production processes but also lessens the environmental impact associated with product creation, paving the way for innovative and eco-friendly solutions. Effectively executed prototyping not only improves the quality of end products but also strengthens the commitment to responsible and sustainable design practices.
Pepin Manufacturing's Commitment to Sustainability
Prototyping has evolved from a functional checkpoint to a strategic pillar of sustainable design. It plays a vital role in reducing design flaws, eliminating resource inefficiencies, and shortening time-to-market—all while minimising environmental impact.
Modern prototyping:
- Reduces Material Waste through digital validation and iterative testing.
- Improves Product Efficiency by identifying opportunities for material optimisation and energy efficiency.
- Enables Lifecycle Thinking, ensuring sustainability is embedded from concept through end-of-life.
With the integration of digital twin technologies, simulation tools, and rapid prototyping methods such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), manufacturers can test products under real-world conditions without generating physical waste—making sustainability a built-in feature, not an afterthought.
Pepin Manufacturing's Leadership in Sustainable Prototyping
Pepin Manufacturing exemplifies how prototype companies can lead in sustainable innovation by embedding green principles across every stage of development. Their approach includes:
- Eco-friendly materials such as biodegradable plastics, recycled composites, and low-emission polymers.
- Advanced 3D printing and CNC machining reduce offcuts, tooling waste, and energy consumption.
- On-demand prototyping supports lean manufacturing, reducing overproduction and inventory waste.
Their facility investments also reflect this ethos—with a focus on energy-efficient systems, waste recovery processes, and sustainable sourcing from verified suppliers.
Industry Trends Reshaping Sustainable Prototyping
Prototype manufacturers now operate within an ecosystem of rapidly evolving practices and technologies. Key trends shaping the future include:
Circular Design Integration
- Manufacturers are shifting toward design for disassembly, reuse, and remanufacturing. Prototypes are increasingly designed with modularity and recyclability in mind, enabling extended product life cycles and compliance with emerging right-to-repair regulations.
AI-Powered Eco-Optimization
- AI-driven generative design tools help engineers automatically create component geometries that use less material, reduce structural waste, and optimise durability—pushing sustainability and innovation simultaneously.
Cloud-Based Collaborative Prototyping
- Platforms like Onshape, Fusion 360, and Siemens NX are enabling remote, cloud-based collaboration. This reduces the need for physical travel and redundant prototyping efforts while centralising lifecycle tracking and sustainability metrics.
Green Certification Standards
- Manufacturers are now aligning with ISO 14001, LEED, Cradle to Cradle, and other environmental certifications that hold prototyping processes accountable to measurable sustainability benchmarks.
Collaborative Innovation Across the Supply Chain
The advancement of sustainable product design increasingly relies on meaningful collaboration among prototype manufacturers and various stakeholders, including designers, engineers, and environmental experts. Pepin Manufacturing actively encourages such partnerships, fostering innovative solutions that address critical ecological challenges. By leveraging collective knowledge and resources, these collaborations can yield groundbreaking products that utilise sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes. Sustainability cannot be achieved in isolation. Pepin Manufacturing champions cross-disciplinary collaboration, working closely with:- Designers and engineers should embed eco-design principles from the outset.
- Sustainability consultants can validate environmental claims and improve lifecycle assessments.
- Suppliers and clients, to ensure material transparency and carbon footprint tracking across the value chain.
These ecosystems foster co-design thinking, resulting in more durable, recyclable, and efficient products.
Aligning with Circular Economy Principles
A fundamental aspect of sustainable product design involves adopting circular economy principles, which advocate for the continuous use of resources through recycling and repurposing. Prototype manufacturers, including Pepin, play an integral role in this model by creating prototypes that can be readily modified and repurposed for various applications. This adaptability not only prolongs the life cycle of products but also promotes a culture of repair and reuse.Empowering the Next Generation of Sustainable Designers
Education plays a pivotal role in preparing the next generation of product designers to adopt sustainable practices, ensuring that environmental responsibility becomes a commonplace aspect of their work. Pepin Manufacturing recognises this obligation and offers workshops, internships, and collaborative opportunities for students and emerging designers. By instilling sustainable principles into early education and professional development, the industry can cultivate innovative thinkers who prioritise eco-friendly design. Education and mentorship are critical in nurturing a new generation of sustainability-minded innovators. Pepin Manufacturing invests in:- Workshops and internships for engineering and design students.
- Partnerships with universities and innovation hubs to develop curriculum around circular design, life cycle analysis, and green prototyping.
- Open innovation challenges that invite young professionals to solve real-world environmental challenges through sustainable product concepts.
This knowledge-sharing ensures that sustainability becomes the default design standard—not an exception.
Conclusion
In conclusion, prototype manufacturers play a crucial role in shaping the future of sustainable product design. Organisations like Pepin Manufacturing not only provide critical services in product development but also exemplify a strong commitment to eco-friendly practices and innovation. As sustainability gains prominence among consumers and industries alike, prototype manufacturers will play a crucial role in shaping a greener future for product design. Their expertise ensures that new products are not just innovative, but also aligned with sustainable practices, positioning them as key players in the evolving landscape of environmentally responsible design.Featured Post
DL Mining Launches Ethereum Contract Participation Service, Helping Users Earn $2K Stable Daily Returns
Zizo Gala-Mkhize-
October 20, 2025
Soapie Teasers
Sister Sites
Most Popular
List of 6,000+ Dofollow Commentluv Blogs FREE (Updated 2025)
January 16, 2025
Five Do’s For a Healthy Turnover That Bolsters Talent-Retention
October 20, 2025
What is Ozempic (semaglutide)? (Updated in 2025)
January 30, 2025
Popular posts
List of 6,000+ Dofollow Commentluv Blogs FREE (Updated 2025)
January 16, 2025
A Wood-Burning Stove in a Tent: A Guide to Safe Hot Tenting
April 08, 2021
Five Do’s For a Healthy Turnover That Bolsters Talent-Retention
October 20, 2025
Footer Menu Widget
Created By Blogspot Theme | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates

Social Plugin