Ad Code
Translate
What is Ozempic (semaglutide)? (Updated in 2025)
Smart strategies for trading on crypto exchanges
How To Find Suitable Properties In Cyprus?
Posture Bra: Improving Back Support and Comfort
All About the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) – 2025 Complete Guide
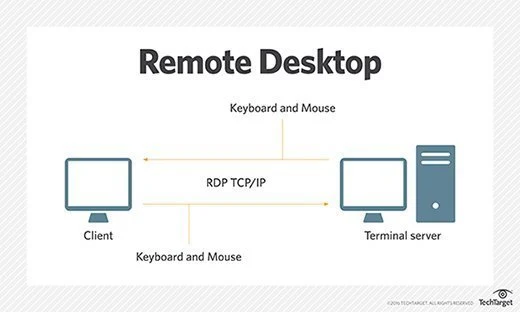
📌 Introduction: What Is RDP?
RDP stands for Remote Desktop Protocol — a widely used technical standard for remotely accessing and controlling a desktop computer or virtual machine (VM) over a network.
Developed by Microsoft, RDP enables users to access the full desktop experience of a remote system — as if sitting right in front of it — using a graphical user interface (GUI).
While RDP is the most common remote desktop protocol, other alternatives include:
- ICA (Independent Computing Architecture) — popularised by Citrix
- VNC (Virtual Network Computing) — an open standard
- PCoIP (PC-over-IP) — used in VMware Horizon environments
| Feature / Protocol | RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) | ICA (Independent Computing Architecture) | VNC (Virtual Network Computing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Developed By | Microsoft | Citrix Systems | AT&T / RealVNC (Open Standard) |
| Primary Use Case | Remote desktop access (Windows & others) | Virtual desktop/application delivery in enterprise environments | Cross-platform remote control |
| Transport Protocol | TCP/IP (Port 3389), UDP (modern versions) | TCP/IP (various ports) | TCP/IP (Port 5900+) |
| Encryption | Built-in (TLS/SSL + NLA) | High-grade encryption (TLS/SSL + Citrix enhancements) | None by default (can be added) |
| Performance | Optimized for Windows environments, good over LAN/WAN | Highly optimized for low-bandwidth and WAN environments | Slower, basic screen sharing |
| Platform Support | Windows (native), macOS, Linux, Android, iOS (via clients) | Windows, macOS, Linux, mobile devices | Cross-platform: Windows, macOS, Linux, Unix, mobile |
| Multimedia Support | Strong (audio, video, device redirection) | Strong (optimized multimedia delivery) | Limited |
| Session Management | Supports multiple concurrent sessions on server editions | Advanced session management (apps and desktops) | Typically one session per connection |
| Licensing | Included with Windows Pro/Enterprise/Server | Requires Citrix licensing (paid) | Open-source/free or commercial options |
| Best For | SMBs, enterprise remote desktop, IT admins | Large enterprises, healthcare, finance, complex VDI deployments | Simple remote support, home users |
| Cost | Included with Windows OS / low cost | Commercial Citrix licenses required | Free (open-source) or low-cost paid |
Originally released for Windows, modern RDP implementations also support macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android devices via clients such as Microsoft Remote Desktop.
🖥️ How Does RDP Work?
RDP works by establishing a dedicated network channel between the remote host (target machine) and the client device (your computer, tablet, or smartphone).
Key technical details:
- Port: RDP typically operates over TCP port 3389.
- Protocol: Uses TCP/IP — the standard protocol for internet and LAN traffic.
- Data exchange:
- Mouse movements
- Keystrokes
- Desktop display rendering
- Clipboard data (optional)
- Printer redirection and file transfers (optional)
- Encryption: Modern versions of RDP use TLS/SSL encryption to ensure secure data transmission.
With this setup, the client device simply renders the desktop graphics, while actual processing remains on the host machine — making RDP ideal for thin clients and cloud-based environments.
🚀 Key Features and Functions of RDP
Modern RDP implementations (Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2019/2022) offer robust capabilities:
✅ High Colour Depth Support — 24-bit colour and up to 4K resolution
✅ Low Bandwidth Optimisation — Performs well even on slow network connections
✅ Session Encryption — Full TLS/SSL encryption for secure sessions
✅ Smart Card Authentication — For enhanced user authentication
✅ Clipboard Redirection — Copy-paste between local and remote sessions
✅ Printer and Drive Redirection — Use local printers and file shares in the remote session
✅ Audio Redirection — Stream audio from the remote desktop
✅ Multi-monitor Support — For power users and enterprise setups
✅ Keyboard Hooking — Allows key combinations (Alt+Tab, etc.) to pass through to the remote session
✅ Session Shadowing — Enables administrators to view/control active user sessions (Enterprise feature)
🔐 How Secure Is Windows Remote Desktop?
Security Overview:
RDP sessions are encrypted by default, protecting against eavesdropping or tampering on the network.
Historical Security Risks:
- Early RDP versions (prior to Windows Vista) employed weak encryption and were susceptible to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
- Modern versions (Windows Vista and later) support TLS/SSL encryption, addressing these weaknesses.
- Network Level Authentication (NLA) is now the default, requiring users to authenticate before a session is established, thereby adding an additional layer of security.
Security Best Practices (2025):
✅ Always enable NLA
✅ Use strong, unique passwords
✅ Limit RDP access via firewalls (VPN or IP whitelisting)
✅ Keep RDP patched and up to date
✅ Monitor for brute-force login attempts
✅ Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) with third-party tools where possible
⚙️ How to Enable Remote Desktop on Windows
Enabling RDP is simple — here’s how:
For Windows 10/11 (Modern Method):
- Go to Settings > System > Remote Desktop
- Toggle "Enable Remote Desktop" ON
- Optionally configure Network Level Authentication (NLA) and user access
📝 Note: Since the Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (1709), this feature is built into Settings — no additional app required.
For Older Versions:
On Windows 7 or earlier,
Use:
Control Panel > System > Remote Settings- Enable Allow remote connections
🌐 How to Connect to a Remote Desktop (Windows Client)
- On the taskbar, click the search bar
- Type "Remote Desktop Connection"
- Launch Remote Desktop Connection (mstsc.exe)
- Enter the IP address or hostname of the target machine
- Click Connect
- Enter your username and password when prompted
- Accept any security certificate warning if the remote machine uses a self-signed certificate
- You're in — enjoy your remote desktop session!
📋 Final Thoughts: Why Use RDP in 2025?
RDP remains one of the most popular, flexible, and cost-effective remote access protocols — suitable for:
- IT administrators managing remote servers
- Remote workers accessing office desktops securely
- Help desk and support teams
- VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) deployments
With modern enhancements such as:
- Better compression algorithms
- Improved latency handling
- Multi-monitor & high-resolution support
- Integration with Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD)
RDP continues to evolve and remain a cornerstone technology in today’s hybrid work and cloud-driven IT environments.


Social Plugin